We are at the cusp of a technological revolution that will shape the future of industries from retail to healthcare: Intelligent Video Analytics (IVA). This innovative technology combines artificial intelligence, machine learning, and computer vision services to not just record, but understand and analyze video data in real time.
It offers an array of opportunities for businesses to enhance operational efficiency, maximize return on investment, and increase safety. With applications spanning sectors such as manufacturing, retail, security, transportation, and healthcare, the potential for transforming operations and reaping significant benefits is immense.
What is intelligent video analytics?
Intelligent video analytics is a technology that leverages computer vision and artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze video footage and generate actionable insights. This involves the use of deep-learning neural networks to identify and understand objects, people, activities, and in real-time or after recording.
Video analytics and AI use algorithms and machine learning to manage and interpret large volumes of video data from surveillance systems. This analysis identifies humans, vehicles, objects, and events. It can also generate descriptions of video content (metadata), providing the foundation for various responses such as safety notifications or starting a recording.
Key Capabilities and Use Cases
Object recognition, object detection and object tracking
Object recognition is a critical computer vision task that identifies and classifies objects present in digital imagery. It seeks to answer the fundamental question, “What object is depicted in this image segment?” This goes beyond just detecting the presence of an object, diving deeper into discerning the specific type or category to which the object belongs. Examples of object recognition can be useful in distinguishing between different types of products on a conveyor belt or identifying different types of flaws.
Object detection is an important computer vision task used to detect instances of visual objects of certain classes in digital images, such as photos or video frames. It provides the most fundamental information needed by computer vision applications, answering the question, “What objects are where?” Examples of object detection include detecting humans, animals, cars, buildings, and more.
Object tracking, on the other hand, allows us to locate and monitor moving objects in videos. Several models and techniques are used today to track things with a high degree of accuracy and efficiency/
For instance, object-tracking algorithms of production line video surveillance and video analytics systems can boost safety and efficiency. Retailers use such techniques to detect theft or suspicious activity. Additionally, computer vision monitors employee safety and performance in manufacturing, alerting them to potential collisions or access to hazardous areas.
Anomaly detection
Anomaly detection in intelligent video analytics involves the identification of patterns in video feeds that deviate from the norm, flagging them as anomalies. This process leverages AI technology to transcend traditional rules-based video analytics, thus transforming a surveillance video system into a real-time loss prevention tool. The use of such a system provides real-time alerts for any anomalous events without needing any pre-configured rules or objects to look for.
From a technical perspective, various machine learning and deep learning techniques have been used to automate the detection of abnormal events in video surveillance applications. For instance, CCTV feeds, automatic detection of traffic violations, and video-based detection of anomalous behavior have all been enabled by these automated systems. This advancement significantly reduces human labor and time, making the process more efficient and cost-effective.
Pattern recognition
Pattern recognition in video analytics involves the application of algorithms and techniques to identify and analyze recurring patterns within video data.
The overall objective of pattern recognition in video analytics is to automate the process of understanding and interpreting video content. This can include a variety of applications, from surveillance systems in healthcare that can identify suspicious activity to automated systems that can analyze traffic patterns on a highway or a smart parking system, to software that can detect health anomalies.
Benefits of intelligent video analytics solutions
-
Higher Operational Efficiency
AI video analytics help improve operational efficiency by providing actionable and valuable business insights. For instance, it can measure unique visit durations and site navigation, differentiate between employee and visitor traffic, and give insights into area occupancy to help optimize space utilization.
-
Improved Staff and Visitors Management
Intelligent video analytics can recognize multiple people across multiple streams simultaneously in real-time, providing efficient people management solutions.
-
Advanced Marketing
Intelligent video analytics can be used to analyze customer behavior, mine historical data, identify patterns and trends, and gather demographic information. This data can be used to make strategic decisions and tailor marketing campaigns to better target potential customers.
-
Customer Experience Boost
Intelligent video analytics can help businesses enhance customer experience. This includes monitoring queue lengths to manage staff levels accordingly, ensuring that customers are served quickly and efficiently, or identifying regular customers and providing personalized services or offers.
As a result, intelligent video analysis can help improve return on investment (ROI) in several ways. For instance, it enables businesses to maximize the utility of their video data by providing actionable and valuable insights into customer behavior or operational efficiency. Additionally, it can minimize losses by improving safety and reducing instances of theft or fraud.
Applications of Intelligent Video Analytics
Manufacturing and Production
Defect detection and detection of anomalies
The AI video surveillance system can detect defects and alert a human supervisor in case of anomalies, who can then review the surveillance video to validate or rectify the operation.
Maintenance and predictive maintenance
Equipment downtimes can be costly, potentially leading to significant losses. Intelligent video analytics technology can reliably and continuously monitor production machinery for indications of wear and tear. The Hepta Airborne and MindTitan collaboration, described in the computer vision case study, explains the maintenance use case in detail.
In other cases, enhanced with IoT and deep learning, intelligent video analysis systems can additionally alert engineers for maintenance well before an issue arises.
Control of Production Cycle Time.
An intelligent video surveillance system has the ability to learn and automatically gauge the duration of each production cycle. Manufacturers can then infer and isolate the optimal practice time for each process. This knowledge is then disseminated to reduce the target time and align with the time to accommodate the conveyor.
Retail and shopping centers
Intelligent video solutions can alert staff about shelf gaps or misplaced products, providing more time for customer service. This real-time data also helps optimize product positions based on consumer purchasing behavior.
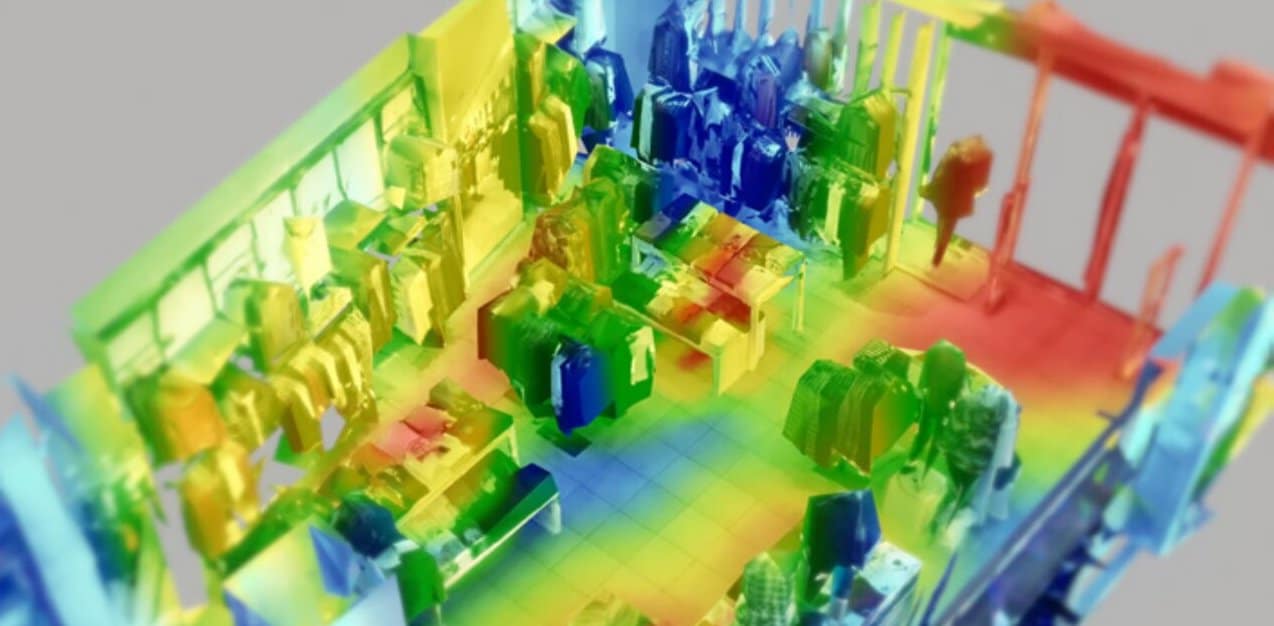
Retail Heat Map
Another example is retail heat map technology that uses color coding to represent traffic volume in different areas. It allows retailers to analyze customer behavior, test merchandising strategies, and adjust store layouts.
Personalization
Additionally, AI video analytics can provide customized services, such as recognizing a returning customer and providing tailored offers based on their previous purchases or preferences.
Video intelligence software can also help businesses measure the effectiveness of their marketing campaigns. For instance, by tracking the number of people who stop to look at a digital signage advertisement, companies can gauge the impact and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Safety and Security
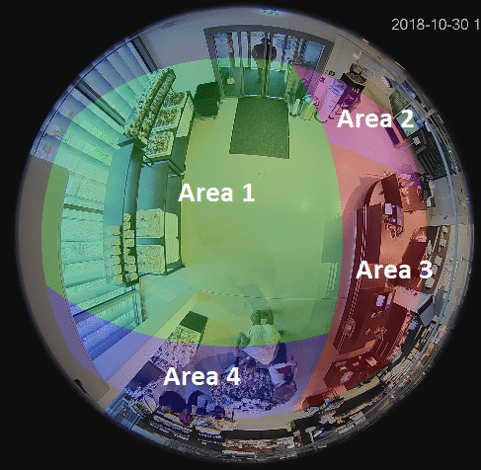
Safety and Security in Retail
Incorporating object-tracking algorithms in retail security systems has revolutionized loss prevention. Through real-time monitoring, these systems detect potential theft or suspicious activities, alerting store personnel or security teams instantaneously. The fusion of computer vision and AI facilitates the proactive detection of threats, enabling swift interventions. Moreover, by analyzing historical data, these systems can predict high-risk timeframes or zones within the store, ensuring higher vigilance during those periods.
Safety and Security In Manufacturing
AI-enhanced security video surveillance systems can aid in tracking objects in a video and detecting them in an image, thus significantly bolstering the security of businesses. However, in the manufacturing sector, security extends beyond merely safeguarding assets; it plays a critical role in ensuring worker safety. Such systems also automatically detect any unauthorized entry/tailgating across various zones in real-time, which can be irreplaceable for processes requiring special equipment.
Visual data derived from security cameras can be amalgamated with other types of data, like those from motion or IR sensors. This data fusion enables the AI system to identify and monitor suspicious items or individuals within a specific monitored area and automatically dispatch relevant alerts to the pertinent authorities. Additionally, by integrating data from various sensors, intelligent video systems provide a comprehensive view of the environment, ensuring timely intervention before accidents occur.
Safety and Security In Anomaly Detection
Anomaly detection in security systems is redefined with the infusion of AI technology. Moving beyond the traditional, rules-based video analytics, these systems possess the intelligence to discern patterns and detect irregularities autonomously. With the capability to monitor vast feeds continuously, AI-driven anomaly detection can flag unusual activities without any predefined conditions. This not only ensures enhanced threat detection but also minimizes false alarms, ensuring resources are focused on genuine threats.
Safety and Security In Transportation
In the realm of transportation, the incorporation of Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR) has streamlined various security functions. ANPR systems, powered by AI, are equipped to rapidly detect and read vehicle license plates. Their precision ensures they can function under diverse conditions, be it varying light or vehicle speeds. Essential for law enforcement agencies, these systems can swiftly trace vehicles of interest, supporting investigations and threat mitigation. Furthermore, by storing and analyzing historical data, they can assist in predicting and preventing potential security breaches.

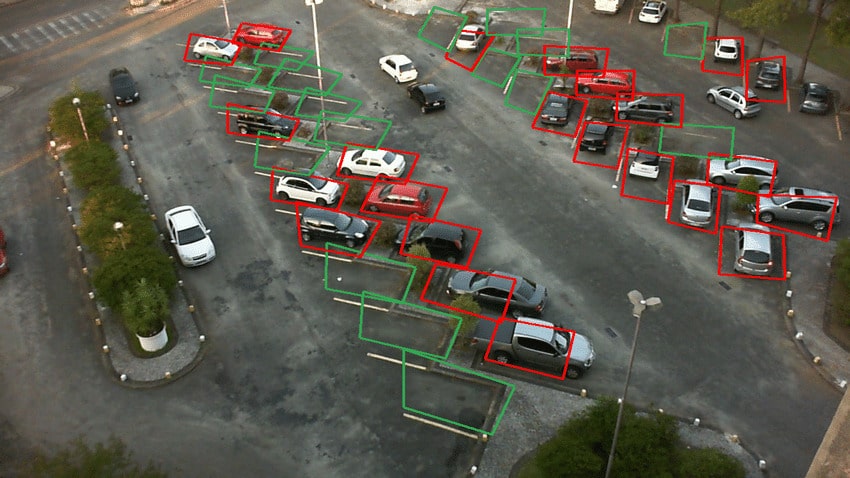
Transportation / Smart Cities
Video object detection autonomously recognizes and tallies vehicles as they enter and depart specific scenes, roadways, and parking areas. This functionality aids individuals in circumventing traffic congestion or fully occupied parking lots. This is particularly beneficial in places with high traffic, such as airports, railway stations, and large corporations.

Healthcare
Intelligent video analytics enhances medical research and diagnostics by catching vital signs that could be missed otherwise.
Video analytics systems can employ high-resolution, long-form recordings for AI development. For example, AI can detect a child’s movement patterns during sleep and wake periods, enabling healthcare professionals to conduct assessments. Companies like Neolook Solutions are using pattern recognition algorithms in their AI systems, such as Screen2Screen Academic Extend, to monitor these patterns and identify potential risks.
Considerations for Implementation
-
Cost of Implementation:
Depending on the scope, implementing an AI Video Analytics system can be costly. This includes expenses for hardware, software, and possibly increased data storage and processing power. Although costs may be offset by the benefits in the long run, the initial investment can be substantial. Furthermore, if the system is to operate in real-time, the network infrastructure may need to be upgraded to ensure smooth and real-time data transmissions. It’s also essential to consider the deployment model, which can vary based on organizational needs. Some might require analytics for a single site, while others may need cross-site analytics for multiple locations. Adding new sites or increasing the number of cameras can lead to additional costs.
-
The Complexity of Setup and Maintenance:
Depending on the sophistication of the system, setup and maintenance can be complex. It might require skilled technicians and continuous updates to ensure the system remains effective against evolving threats. For instance, video resolution, bitrate, and frame rate will factor into the recommended supporting hardware for your video analysis integration.
Besides, it’s necessary to consider the deployment model. Different deployment models like on-camera edge, cloud or server-based, or a hybrid of the two can have varying complexity levels.
Furthermore, there may be soft costs associated with user training and system deployment, like the cost of a third-party systems integrator. Deploying software in the cloud or on-premises poses different prices. In contrast, an on-prem solution provides IT departments with greater flexibility over configurations and updates. Still, the associated costs of upkeep are not insignificant.
Edge computing vs. cloud deployment
Edge-based analytics, by definition, processes video data analytics within the device itself, such as a camera (IoT on the edge). This eliminates latency issues and can provide real-time or near-real-time insights, which can be beneficial in applications where immediate response is required, such as intrusion, motion detection, or fire detection. It is also a more privacy-preserving approach, as data does not leave the local device unless necessary. However, the edge might need help with large-scale analytics projects or the integration of complex AI technologies due to its limited computational resources.
On the other hand, cloud-based analytics uses remote public or private computing resources, known as the “cloud,” to analyze data on demand. This approach allows for powerful and scalable data processing, making it more suitable for large-scale analytics projects and the integration of AI and machine learning technologies. The introduction of 5G and its benefits, such as low latency, fast speeds, and increased capacity, will significantly enhance the performance of cloud-based analytics, making real-time data streaming possible.
However, when it comes to choosing between edge and cloud for intelligent video analytics implementation, several factors need to be considered. These include the sensitivity and volume of the data to be processed, the need for real-time analytics, the available network bandwidth, and the computational resources and storage capacity available on edge devices.
Moreover, it’s worth mentioning that edge and cloud analytics don’t necessarily have to be mutually exclusive; a hybrid approach may be most suitable for specific applications. In this model, time-sensitive data is processed on the edge for immediate insights, while non-time-sensitive data is sent to the cloud for more comprehensive analysis.
Implementing intelligent video analytics involves a careful evaluation of the organization’s specific requirements and constraints, the capabilities and limitations of edge and cloud analytics, as well as factors such as cost, cybersecurity, and privacy considerations.
Data management and integration
-
Data Privacy Concerns:
The use of video analytics often involves collecting and analyzing vast amounts of data, some of which can be sensitive. This can raise concerns about privacy, particularly when facial recognition or license plate recognition technology is used. Complying with data protection regulations and ensuring customer consent can pose challenges.
-
Dependence on Quality of Video:
The effectiveness of video analytics relies heavily on the quality of the video feed. Poor resolution, low light conditions, or obstructions can affect the accuracy of analysis and lead to false positives or negatives.
Cybersecurity risks
Cybersecurity risks for intelligent video analytics systems primarily stem from increasing reliance on AI and cloud-based technologies, as well as the highly interconnected nature of such systems. They include:
- Data breaches: Breaches can occur due to vulnerabilities in the system, and they can lead to the leakage of sensitive information, such as video footage and analytics data.
- Ransomware attacks: These are attacks where hackers encrypt the data and demand a ransom for its decryption. The rise of ransomware attacks poses a significant threat to businesses, including those using intelligent video analytics.
- Cloud third-party threats: As video analytics often leverage cloud computing for data storage and processing, they become vulnerable to third-party threats. Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in cloud service providers to gain access to sensitive information and infrastructure.
- Zero-Day Vulnerabilities: These are vulnerabilities in the software that are unknown to the software developers. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by hackers to breach the system before the vulnerability is patched.
To overcome these challenges:
- Focus on Privacy Protection: GDPR-like data privacy laws may become common, emphasizing the need for enhanced privacy protection. This may include obscuring faces in video footage while maintaining a secondary protected data stream for evidentiary purposes.
- Improve Cybersecurity Awareness and Adopt Zero Trust: To counter cybersecurity threats, organizations should adopt a zero-trust approach where all network traffic is treated as potentially threatening, even traffic that originates from within the organization’s network.
- Regular Patching and Updating: One of the most effective ways to prevent cyber attacks is regular software patching and updating. This can help in mitigating the risk of zero-day vulnerabilities and other exploits.
- Invest in Cybersecurity Training: Regular cybersecurity training can help reduce the threat posed by human errors and misconfigurations, which are often a significant source of security breaches.
Privacy regulations
Intelligent video analytics involves the collection and storage of sensitive data like people’s faces, license plates, and biometric data, triggering significant privacy and data protection concerns.
A foremost concern revolves around security incidents and the potential misuse of collected data. If mishandled or accessed by unauthorized parties, it can be used for malicious purposes such as identity theft or stalking. Additionally, there’s a risk of false positives since AI technology isn’t flawless. A false alarm might result in a person being wrongly accused of a violation or crime, which can have profound implications. Also, privacy regulations pose a challenge to organizations using AI video analytics as many countries enforce stringent laws around personal data collection, storage, and use. Failure to comply can result in substantial fines and other penalties.
For instance, the data privacy landscape in 2023 has already witnessed significant developments, with organizations like Meta and Microsoft being fined for non-compliance with GDPR. Global privacy regulations like GDPR in Europe, CPRA in the US, and PIPEDA in Canada continue to become more stringent in response to the growing amount of personal data being generated and stored by companies.
Role of human operators
-
Bias in AI Algorithms:
Like all AI systems, video analytics can be subject to bias. This occurs when the data used to train the AI system is not fully representative. This could lead to a disproportionate number of false positives or negatives for specific groups.
-
Need for Human Oversight:
Despite its advanced capabilities, AI Video Analytics still requires human oversight to confirm its findings, particularly in critical scenarios. This mitigates the risk of overlooking a threat due to a system error or misinterpretation.
Conclusion
Intelligent video analytics stands at the forefront of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, wielding the power to transform how businesses function. Its vast array of applications, from anomaly detection and pattern recognition to people management and customer insights, provide numerous avenues for enhancing efficiency, security, and profitability. It’s not just a technology, but a business tool, designed to offer actionable insights, improve decision-making processes, and provide a competitive edge in today’s digital world.
However, navigating the marketplace of readily available intelligent video analytics solutions can prove challenging, especially without a deep technical understanding. Further complicating this is the fact that off-the-shelf solutions might not align precisely with your requirements. They typically come packed with additional features that could be excessive for your needs, potentially creating more complexity. Additionally, these applications might necessitate the use of highly sophisticated, and consequently, exorbitantly priced hardware.
Such factors can considerably impact the outcomes you strive for with your video analysis solution. Among other benefits, a tailored solution is often the best way to ensure the highest degree of accuracy for your specific scenario.

