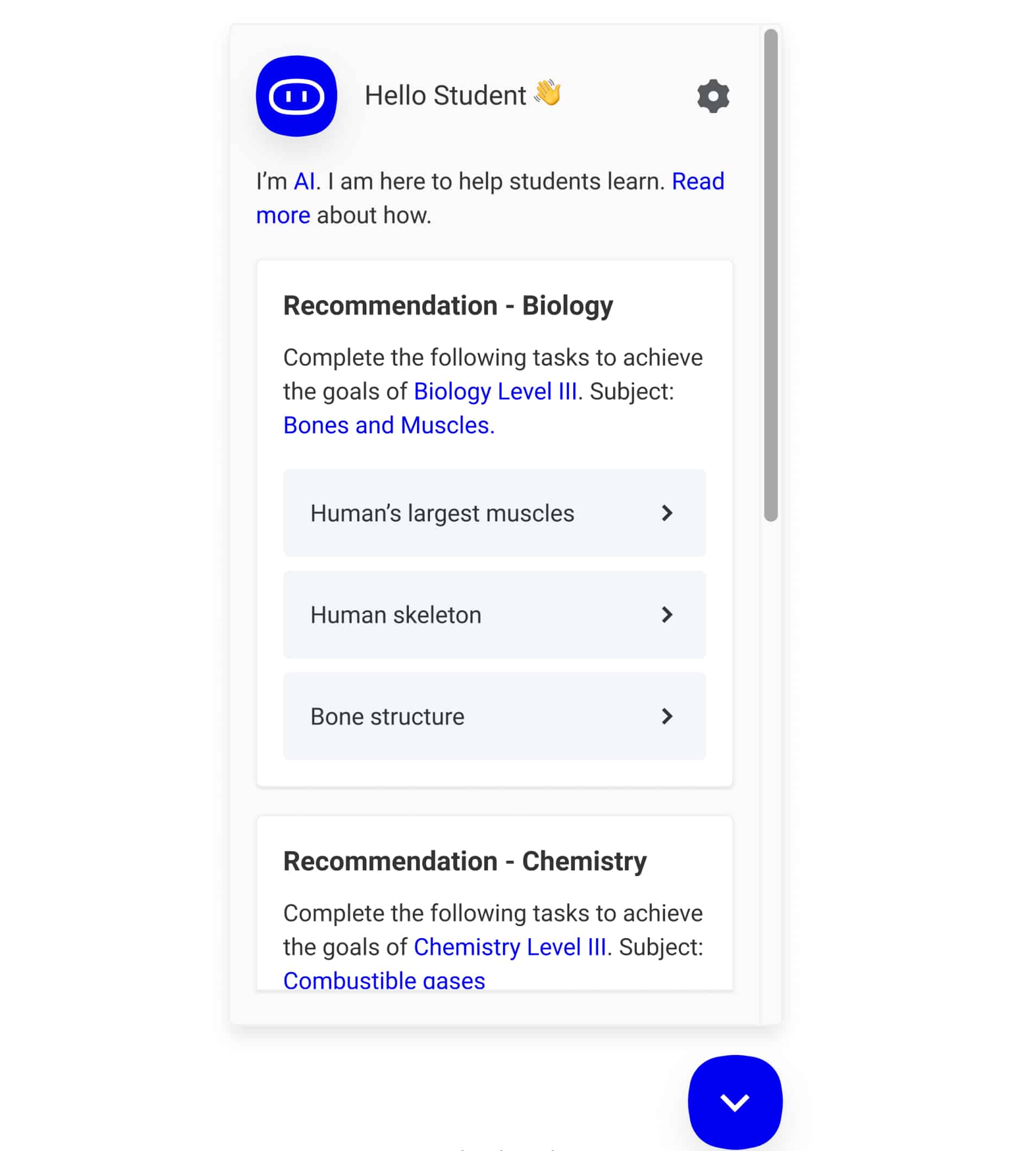
3. Smart content creation
AI in education can assist with the content that will make teaching and learning more comfortable. Starting with question-answer pairs that could be used for texting or training, and ending with complex study environments.
Digital lessons
AI can analyze a big topic and then divide it into smaller, easy-to-grasp parts; make study guides or digital textbooks from those pieces, all within the framework of digital learning. Exercises as a part of these digital lessons could also be produced with the help of AI: computer vision can be used to take the necessary parts from learning materials, and natural language processing algorithms afterward can be trained to create different types of learning materials: fill-the-gap questions, flashcards with definitions, multiple and single choice questions.
AI-powered Educational Games
Modern AI-powered games enhance this by providing personalized learning experiences through adaptive programming. These games can adjust to each student’s learning pace and style, offering customized challenges and feedback. This technology not only makes learning more engaging but also more effective, as it can pinpoint areas where students need more help and offer tailored support. AI in educational games represents a significant advancement from traditional methods, making learning both fun and highly individualized.
Example: Duolingo
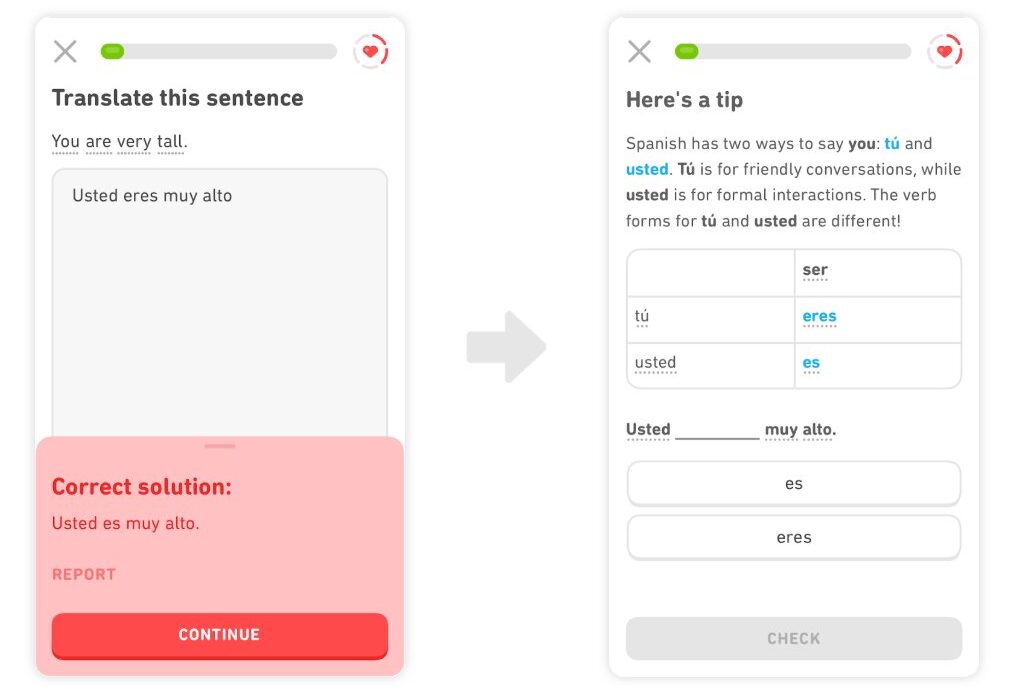
Information visualization
To perceive information, students can lean on AI-powered simulations, visualizations, and study environments. Moreover, those educational environments are integrated with AI-based stealth assessment. It means that the process of assessments is integrated seamlessly into the environment so that the student is unaware of being assessed.
Connecting with Environments
AI in education doesn’t just help to illustrate the material, it extends beyond classroom learning providing hands-on experience with AI helps students understand and solve ecological problems. For example, middle school students in Maine use an AI bird feeder to learn about species visiting it. Alongside, children learn how AI identifies birds, what are the reasons behind mistaken identification. They can also connect with broader projects, such as observing puffins off the coast of Maine, where AI helps researchers capture extensive data.