Machine learning development provided businesses with benefits reaching from US$250,000 to US$20 million, or even a long-term investment – a few billion dollars over several years, Deloitte claims.
Machine learning (ML) algorithms process raw data for meaningful insights to quickly solve complex business issues. Machines learn from the data iteratively, finding hidden insights and patterns without being programmed to do so.
Machine learning technology enhances business scalability and operations. Growing production volumes, data availability, affordable computational processing, and data storage have led to a massive machine learning boom. Therefore, enterprises can now benefit by understanding how businesses can use machine learning techniques and implement the same models in their own processes.
What is machine learning?
Machine learning is an extensive term and may include different techniques. But ultimately, it’s all about bringing value to society or business.
So, what is machine learning? The shortest version: imagine it as a production line of a kind. A machine learning model can produce output from data input. To develop properly, machine learning algorithms need training data to learn from.
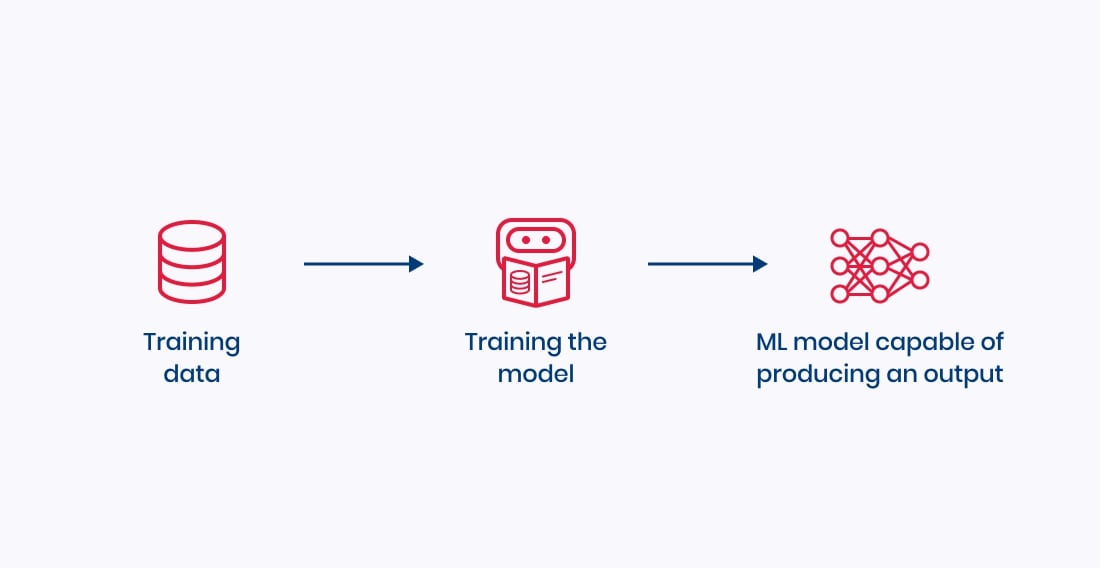
For those who want more: Machine learning systems process input (e.g., information from your CRM, databases, spreadsheets) and provide an output (e.g., finding fraudsters, handling claims, classifying what the customer asked). Using sample data, the machine learning team teaches algorithms to produce the required output. For most businesses, that’s it, and there is no need to delve deeper. Just talk to your ML partner for specifics as needed.
Machine learning vs. artificial intelligence vs. deep learning
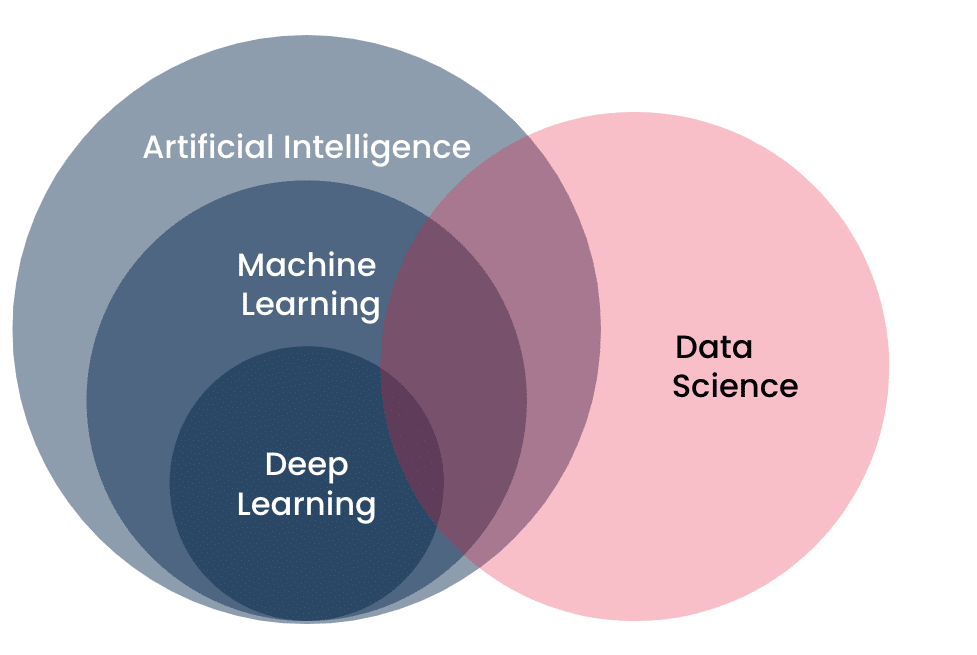
Simply put, artificial intelligence (AI) deals with tasks requiring human intelligence. Machine learning (ML) is a subset of AI that learns from data and makes predictions, thus solving tasks.
Check the picture below: deep learning is a part of machine learning, which itself is a branch within the broader realm of artificial intelligence. Artificial intelligence and data science also intersect substantially, although each encompasses aspects beyond the other. With these layered relationships, it’s understandable why artificial intelligence, machine learning, data science, and occasionally deep learning are used interchangeably. This arises because the most significant advancements and innovations often occur where these fields converge – at the intersection of AI, machine learning, and data science. Hence, their terminologies often overlap in discourse, and it’s typically accurate to a sufficient degree to use those terms interchangeably.
What is machine learning used for?
People often consider machine learning (ML) a fantastic solution to many problems. The truth is that machine learning looks close to magic, and it can solve many issues or at least improve many situations. But AI projects will be successful if a leader understands how to make a business work with machine learning.
Machine Learning algorithms focus on four fundamental methods:
- Unsupervised Learning allows algorithms to autonomously discover patterns in untagged data, ideal for exploratory analysis.
- Supervised Learning involves training algorithms with annotated data to generate predictions or classifications on new datasets.
- Semi-Supervised Learning merges a small portion of labeled data with a larger set of unlabeled data, offering a balance between efficiency and accuracy.
- Reinforcement Learning trains agents to make decisions through trial and error to maximize rewards, commonly used in fields like robotics and gaming.
The true power of machine learning lies in its capacity to resolve complex issues through classification (sorting data) and regression (forecasting continuous outcomes), especially when integrated with human-in-the-loop (HITL) systems. HITL enhances the precision and relevance of supervised learning by incorporating human feedback, making it effective for tasks that require a blend of automation and human expertise. This approach enables businesses to automate processes, extract valuable insights, and make informed predictions, thereby improving operational efficiency.
Trends and patterns identification
Machine learning algorithms are able to review large volumes of data and identify patterns and trends that might not be obvious to a human. A machine can detect complex connections and correlations in the data, allowing it to predict, for example, the need for equipment maintenance. Using sensor and/or visual data AI and computer vision system can notice the trend in key indicators suggesting degradation of a component long before a person would. Thus, the technology is effectively used in data mining, specifically on a continual, ongoing basis.
Process automation
Machine learning models empower rapid adaptation of processes without human intervention. Moreover, machine learning algorithms can improve over time. Typically efficiency and accuracy grow because of the ever-increasing data to learn from. That is to say, the machine learning algorithms or programs have more “experience,” which provides, in turn, better decision making or predictions.
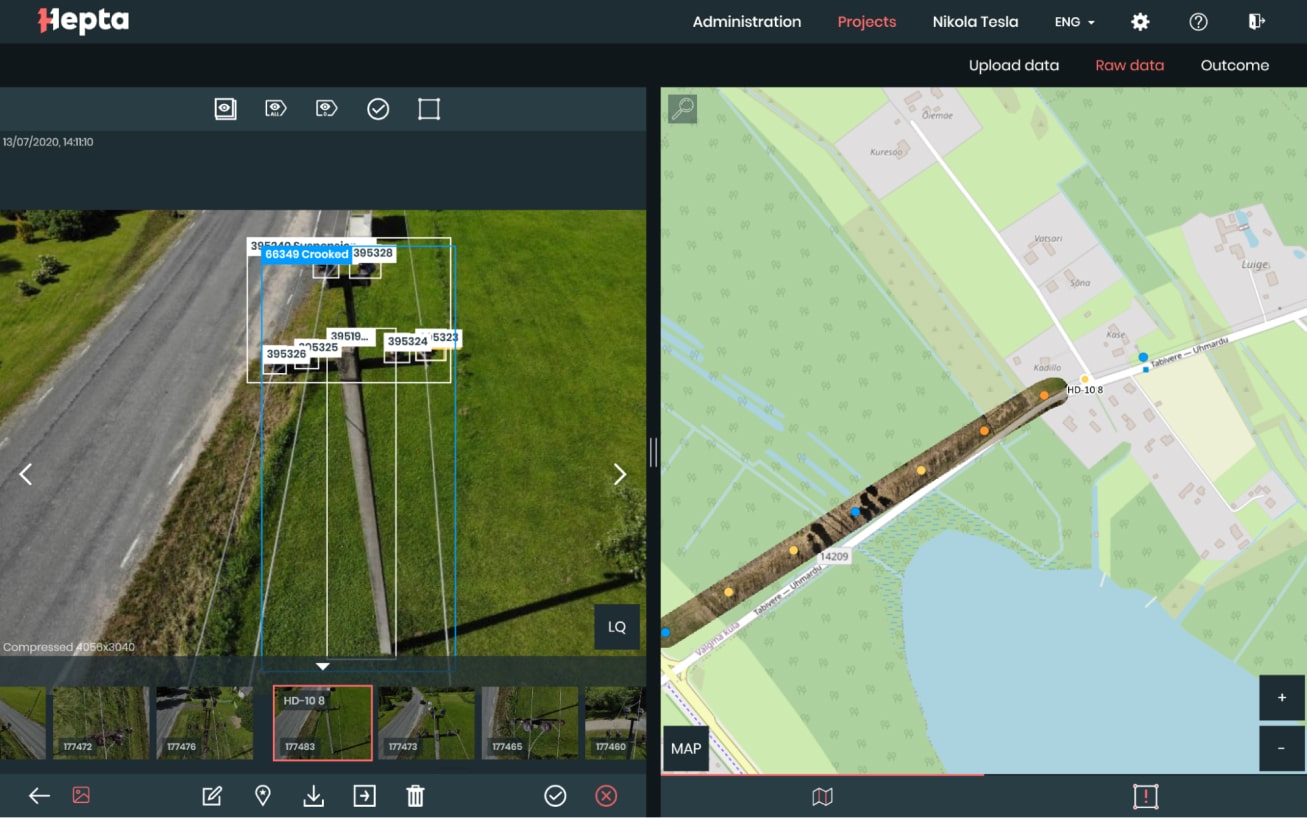
An example of this automation and improvement over time through machine learning is AI for Hepta Airborne. It detects transmission network faults on photos taken by drones flying overhead (you can find out details by reading this computer vision case study). When the ML system suspects a faulty detail, it flags the image. Then, the human specialist reviews the case, providing feedback and a decision. The reviewed cases then join the training examples; consequently, the machine becomes more efficient over time.
Handling multidimensional and high-variance data
Machine learning algorithms can handle multidimensional and high-variance data, and they can do this in dynamic or uncertain environments. Admittedly, it is not the most straightforward task for the machine learning team. However, in this case, a successful application of machine learning can provide significant time and money savings.
An example of this application is the police patrol placement system. Forecasts of the locations are made by looking at past cases’ historical data from up to four years prior, also considering economic situation, demographics, and even weather conditions.

Examples of machine learning use cases in business
Staying informed about the current applications of machine learning and artificial intelligence is crucial for tech professionals to maintain their relevance and address today’s business demands. Key areas to focus on include:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Advancements in NLP are significantly enhancing chatbots, language translation, and sentiment analysis, driving the need for machines to better comprehend human language.
- Artificial intelligence and Internet of Things (IoT): AI is making IoT systems more intelligent, efficient, and capable of handling complex data analysis and autonomous decision-making.
- Automated Machine Learning (AutoML): The rise of AutoML is making machine learning more user-friendly and efficient by automating key processes, thereby enabling broader accessibility and improving the development of models.
Whether you are an e-tailer or a healthcare provider, ML could work for you: each industry has a list of specific use cases worthy of separate and detailed articles. A business in any industry that produces data (which means literally every business) could discover its own AI application and a way of machine learning implementation.
- For example, machine learning models and AI in utilities could enable more efficient energy production and forecast utility consumption.
- Machine learning and AI in manufacturing improve production through assembly line automation and help maintain workplace safety.
- AI in telecom creates exceptional customer service for the best client experience while saving companies money.
- AI in aviation not only determines ticket prices but also ensures air traffic control and air traffic management.
- Machine learning and AI in finance and banking often use natural language processing (technology that lets machines understand human language, verbal or written) to make conversational AI banking systems. These systems ensure customer support. However, it could be used for financial advisory or regulatory compliance in the financial sector.
- A wide variety of applications is found for AI in the public sector. For example, tax fraud detection, road traffic accident prediction, or emergency response.
- Artificial Intelligence in Retail and eCommerce analyzes, for instance, user behavior, whereas AI in education supports personalized learning and automates test checking.
- In pharmaceuticals and healthcare, AI and machine learning improve and speed up diagnostics, drug discovery, and testing.
- Cybersecurity is another area where machine learning is making a substantial impact. By recognizing patterns and adapting to new threats in real-time, machine learning reduces the need for constant human observation, allowing businesses to focus on other critical areas. However, the growing sophistication of cyberattacks means that the demand for machine learning experts in cybersecurity will continue to rise. Ensuring strong security measures will be crucial for businesses to protect their data and maintain trust with their customers.
Enhanced customer experience
If you have customers — AI could help them (hence, your business). The lag that annoys customers could happen between their needs and business responses. Automated chatbots, callbots, and other personalized messaging systems, empowered with deep machine learning and natural language processing models, such as AI-powered customer sentiment analysis, can solve these issues by providing timely, tailored customer experiences. Moreover, the efficiency of customer support teams (hence, customer satisfaction) increased through the cutback of manual workflows.
Error reduction
The machine only understands accuracy. Once given good instructions, the machine follows them precisely. It means that “human factor” errors could disappear from your automated processes. A proper machine learning algorithm will free your employees from repetitive and dull tasks. Those tasks will go to the background as they won’t require human involvement, at least a significant one.
Automation
As mentioned above, automation is the output of AI implementation. Moreover, that automation can enhance almost every business process, from communications and marketing to internal onboarding and support. For example, in manufacturing processes AI and ML automation can improve yield by up to 30% and reduce scrap rates and testing costs.
Furthermore, employees could discover resources for ideas and projects that manual workflows previously took. Automated processes allow replacing the routine of tiny tasks with the freedom to work with more creative and complex tasks.
Tackling complex problems
Machine learning allows dedicating precious time to more complex problems since this technology delivers solutions and a possibility of scaling.
Operational efficiency growth
Another benefit of machine learning is efficiency increase as a consequence of repetitive tasks automation and error reduction. Chatbots can efficiently work 24/7; machines can process overwhelming amounts of data without burning out. Thus, the estimated improvement in business productivity by using AI reaches 54%.
Decision making
Smarter decision-making is also a goal of AI and ML implementation. Humans cannot process and coordinate the avalanche of data as quickly and well as machines do. A machine learning algorithm is able to translate raw data into an objective decision. AI delivers data, analyzes trends, and forecasts results while taking human emotion out of it.
Watch out for machine learning pitfalls
Looking ahead, machine learning is poised to play an even more significant role in industries like healthcare and cybersecurity. As these fields face increasingly complex challenges, the ability of machine learning to adapt and learn from vast amounts of data will be invaluable. However, businesses must also be prepared for the challenges associated with machine learning implementation, such as the need for large datasets and the potential for algorithmic errors. Addressing these challenges requires careful planning and expert guidance.

Probability of errors
An error within an machine learning algorithm can cause poor, skewed, or just plain undesirable results. Unfortunately, errors do occur, and developers still cannot 100% foresee and negate them. What’s more, these errors can vary significantly. For example, a faulty sensor could generate a flawed data set. If this inaccurate data goes into the machine learning algorithm, it will cause erroneous results. For instance, the related product recommendations could not be even closely related or similar.
The autonomous and relatively independent nature of machine learning causes errors to be spotted late in the process. Since a machine learning program is built to reduce or eliminate human involvement, an error may not be discovered immediately. When the problem is detected, finding its root may take time and effort. Measures to correct the error and eliminate any damages that arose from the situation could take even more time.
However, even with sometimes time-consuming force majeure and correction processes, machine learning still could be better than the alternatives in terms of efficiency and productivity.
Data acquisition
While some machine learning use cases require massive amounts of training data, most of the time, good results can be achieved by using large publicly available data sets and fine-tuning the system on good quality, domain-specific data set.
While collecting massive data sets can be complex and time-consuming, ensuring high quality in domain-specific datasets requires some expertise. It often leads to the necessity to adjust the data collection process to achieve better results. On top of that, one needs experience to know what adjustments are required.
Data problems are better to solve early on and collect and label the correct data in the right way to avoid potentially significant issues later in the process.
Time and resources for machine learning to provide results
As mentioned before, data acquisition alone is time-consuming. Thus, there might be a period when the algorithm isn’t ready enough to satisfy your needs. The process of machine training on new data is similar to the training period required for a new employee. Fortunately, a machine learning engine can’t give its 2-week-notice.
Processing vast amounts of data and running computer models takes much computing power, which usually is costly. So, it’s essential to consider the time and money necessary for the technology development to a point where it will be profitable before machine learning implementation. However, the exact amount of time depends on the data source, the nature of the data, and the way it is used. Consequently, it is better to consult with machine learning experts first to avoid later concerns.
A good machine learning team would also advise whether you’ll need new data to generate.
Result interpretation
Interpretation of the results generated by machine learning algorithms could be a challenge. Therefore, businesses should be careful in choosing algorithms for their purposes.
Given the potential for errors and the complexities involved in machine learning, it is essential for businesses to engage with experts when implementing these technologies. Expert guidance can help identify potential pitfalls early, ensure that the correct data is collected and used, and provide strategies for managing and mitigating risks. This proactive approach can save significant time and resources, allowing businesses to reap the benefits of machine learning while minimizing the chances of costly mistakes.
Conclusion
The advantages of machine learning definitely make this technology a powerful tool for creating a competitive advantage for businesses. However, machine learning implementation is not pitfall-proof. From ensuring data accuracy to managing algorithmic errors, the road to successful implementation is fraught with potential obstacles.
It is logical to weigh the time and resources required to implement machine learning against the potential benefits. While the technology offers significant advantages, including automation, improved decision-making, and enhanced operational efficiency, the initial investment can be substantial. Companies should conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis and consider long-term gains versus short-term expenditures.
To prevent problems and make educated decisions, it is wise to consult machine learning gurus first. They can help in making these assessments more accurate and aligned with business goals.

